Securing Trust: The Definitive Guide to AI Voicebots in Banking Emergency Alerts

Index
Introduction: The New Frontier of Financial Security and Communication
- 1.1 The High Stakes of Communication Latency
- 1.2 A Brief History of Bank-to-Customer Communication
- 1.3 The Thesis: Why Voice AI is the Inevitable Next Step
- Chapter 1: Deconstructing the Failures of Traditional Alerting Systems
- 2.1 The SMS Channel: Convenience vs. Critical Vulnerabilities
- 2.2 The Email Channel: The Abyss of the Cluttered Inbox
- 2.3 Mobile App Push Notifications: The Double-Edged Sword of Immediacy
- 2.4 The Manual Call Centre: The Human Bottleneck in a Digital Crisis
- Chapter 2: A Deep Dive into AI Voicebot Use Cases for Banking Emergencies
- 3.1 Use Case: Real-Time Fraud Detection and Mitigation
- 3.1.1 Anatomy of a Voicebot-Led Fraud Intervention
- 3.1.2 Handling Complex Fraud Scenarios
- 3.2 Use Case: Proactive Management of Service Outages and Downtime
- 3.2.1 Tiered Communication Strategies
- 3.2.2 The Post-Resolution Follow-up
- 3.3 Use Case: Navigating the Complexities of Data Breach Notifications
- 3.3.1 Meeting Global Regulatory Demands with AI
- 3.3.2 Delivering Empathetic and Actionable Guidance
- 3.4 Use Case: Business Continuity During Natural Disasters
- 3.5 Use Case: Urgent Compliance and Account Security Mandates
- 3.1 Use Case: Real-Time Fraud Detection and Mitigation
- Chapter 3: The Architecture of Trust in AI-Driven Communication
- 4.1 The Pillars of Digital Trust: Personalisation, Proactivity, and Transparency
- 4.2 Engineering Empathy: The Nuances of Conversational Design
- 4.3 The Human-in-the-Loop Model: The Perfect Symbiosis
- Chapter 4: A Strategic Roadmap for Implementing an AI Voicebot Alert System
- 5.1 Phase 1: Defining Objectives and Measurable KPIs
- 5.2 Phase 2: Selecting the Right Technology Partner
- 5.3 Phase 3: Secure Data Integration and Infrastructure
- 5.4 Phase 4: Crafting Intelligent and Dynamic Conversation Flows
- 5.5 Phase 5: Pilot Testing, Learning, and Iteration
- 5.6 Phase 6: Scaling for a Resilient Future
- Chapter 5: The Tangible ROI: Building the Business Case for Voice AI
- 6.1 Quantifying Cost Reductions
- 6.2 Measuring Gains in Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- 6.3 De-risking the Enterprise
- Conclusion: The Future of Secure Banking is Not Just Digital, It's Vocal
- References
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Introduction: The New Frontier of Financial Security and Communication
1.1 The High Stakes of Communication Latency

In the hyper-connected financial ecosystem of today, time is not just money; it is the very fabric of security and trust. A fraudulent transaction can drain an account in minutes. A system outage can lock millions of customers out of their funds, sparking panic. The delay between a critical event's occurrence and a customer's awareness of it is known as communication latency. This latency is a bank's single greatest vulnerability in a crisis. A delay of an hour can lead to irreversible financial loss. A delay of a day can lead to irreparable brand damage. For decades, financial institutions have wrestled with this problem, attempting to close the gap with the best tools available. But as threats have grown in speed and sophistication, the tools have struggled to keep pace.
1.2 A Brief History of Bank-to-Customer Communication

The evolution of bank alerts is a mirror of technological progress itself. It began with the formal, slow-moving postal letter, suitable for monthly statements but utterly useless for emergencies. The telephone call from a human agent offered immediacy but was impossible to scale. The 1990s and 2000s brought the digital revolution: email and SMS messages. These were heralded as the solution—instant, cheap, and scalable. For a time, they were effective. But their ubiquity became their downfall. Today, a customer's digital life is a maelstrom of notifications. In this environment of overwhelming noise, critical alerts have lost their power to command attention.
1.3 The Thesis: Why Voice AI is the Inevitable Next Step
We stand at a new inflection point. The limitations of passive, text-based systems have become glaringly apparent. To restore immediacy and cut through the noise, banks must re-engage the most fundamental and attention-grabbing form of human communication: voice. However, leveraging voice at the scale of modern banking is impossible with human agents alone. This is the precise juncture where Artificial Intelligence (AI) Voicebots enter the narrative.
AI-powered voicebots are not a mere upgrade to existing systems; they represent a paradigm shift. They combine the piercing immediacy of a phone call with the infinite scalability of software. They merge the personalisation of a one-on-one conversation with the efficiency of automation. This guide will provide a comprehensive exploration of how AI voicebots are becoming the cornerstone of emergency alert strategies for forward-thinking banks, delving into their technical applications, the trust they engender, the strategy for their implementation, and the undeniable return on investment they provide.
Chapter 1: Deconstructing the Failures of Traditional Alerting Systems
To appreciate the revolution, we must first dissect the old regime. Each traditional channel, while once innovative, now carries inherent flaws that make it unsuitable as a primary tool for high-stakes emergency alerts.
2.1 The SMS Channel: Convenience vs. Critical Vulnerabilities

The Short Message Service (SMS) was the workhorse of mobile alerts for two decades. Its beauty lies in its simplicity and universality—nearly every mobile phone can receive a text.
- The Pros: Ubiquitous reach, low cost, and perceived immediacy.
- The Cons & Vulnerabilities:
- "Alert Fatigue": The average person receives dozens of texts a day, from marketing promotions to delivery updates. A critical bank alert can easily be swiped away with the rest, its urgency completely lost.
- The "Smishing" Epidemic: SMS phishing, or "smishing," has exploded globally. Fraudsters send cleverly disguised texts mimicking bank alerts, tricking customers into divulging credentials on fake websites. This has trained savvy customers to be deeply suspicious of any link in a text, even legitimate ones, thus delaying their response.
- SIM Swapping Attacks: A determined fraudster can trick a mobile carrier into porting a victim's phone number to a new SIM card. Once they control the number, they receive all the SMS alerts and one-time passwords (OTPs), effectively locking the real customer out while they drain the account. This makes SMS a fundamentally insecure channel for verification.
- Lack of Confirmation: An SMS gives a "delivered" receipt, but this provides no information on whether the message was read, understood, or actioned. The bank remains blind to the customer's status.
2.2 The Email Channel: The Abyss of the Cluttered Inbox
Email remains the backbone of formal business communication, but it is one of the least effective channels for time-sensitive emergencies.
- The Pros: Ability to convey detailed information, universal adoption, and a formal record of communication.
- The Cons & Vulnerabilities:
- Extremely Low Urgency: Emails are checked infrequently. Open rates for non-marketing emails are still shockingly low, and a critical alert could sit unread for hours or days.
- Aggressive Spam Filters: To protect users, email clients like Gmail and Outlook use highly aggressive spam filters. Legitimate, automated alerts from banks are often miscategorised and sent directly to the spam folder, never to be seen by the customer.
- Sophisticated Phishing: Phishing emails are an art form for criminals. They can be visually indistinguishable from official bank communications, leading to credential theft on a massive scale. The risk is so high that security experts universally advise against clicking links in unsolicited emails.
- Data Overload: For complex situations like a data breach, a long, text-heavy email can be overwhelming and confusing for a stressed customer, leading to inaction or misunderstanding.
2.3 Mobile App Push Notifications: The Double-Edged Sword of Immediacy
For customers who have the bank's mobile app installed, push notifications seem like the perfect solution—instant, direct, and on the device they use most.
- The Pros: Instant delivery, deep-linking into the app for immediate action, and a secure channel controlled by the bank.
- The Cons & Vulnerabilities:
- Permission-Based: The effectiveness of push notifications hinges entirely on the customer having (a) installed the app, (b) enabled notifications, and (c) not become desensitised to them. A large percentage of users disable notifications to reduce distractions.
- Notification Blindness: Similar to alert fatigue, users are bombarded with notifications from dozens of apps. A bank alert is just one more pop-up to be dismissed without a thought.
- No Fallback: If a customer has their phone on "Do Not Disturb," has disabled notifications for the app, or doesn't have a stable internet connection, the alert simply fails to deliver. There is no built-in mechanism to confirm receipt.
- Limited Information: Push notifications are, by design, short. They are ill-suited for conveying complex instructions or the gravity of a situation.
2.4 The Manual Call Centre: The Human Bottleneck in a Digital Crisis
What about a good old-fashioned phone call from a human agent? Surely that cuts through the noise.
- The Pros: The highest potential for empathy, trust-building, and resolving complex issues.
- The Cons & Vulnerabilities:
- Utterly Unscalable: A medium-sized bank might have millions of customers. A system-wide outage would require a call to every single one. A call centre with a few hundred agents could not even begin to tackle this task in a timely manner. It would take weeks.
- Prohibitive Cost: The operational cost of maintaining a 24/7 call centre large enough to handle a crisis is astronomical. The cost per call is orders of magnitude higher than any automated solution.
- Inconsistency of Message: Different agents may describe the same situation in slightly different ways, leading to confusion. Some may sound more alarmed than others, causing unnecessary panic. An automated system delivers a perfectly consistent, quality-controlled message every time.
- Human Error and Availability: Agents work in shifts, get tired, and make mistakes. A crisis doesn't wait for business hours. An automated system is ready to execute flawlessly 24/7/365.
The conclusion is inescapable: every traditional channel has a fatal flaw in the context of a large-scale, time-critical emergency. A new approach is not just preferable; it is necessary.
Hotel AI-Intervo.ai
Chapter 2: A Deep Dive into AI Voicebot Use Cases for Banking Emergencies
AI voicebots are not a monolithic solution but a flexible platform that can be deployed in highly specific ways to address different types of crises. Their effectiveness comes from applying a tailored conversational flow to each unique scenario.
3.1 Use Case: Real-Time Fraud Detection and Mitigation

This is the quintessential and most impactful use case for emergency voicebots. Modern fraud—whether affecting Faster Payments in the UK, Zelle in the US, or SEPA transfers in Europe—happens at machine speed; the response must be equally fast.
3.1.1 Anatomy of a Voicebot-Led Fraud Intervention
Consider a "Card Not Present" (CNP) transaction, a common type of online card fraud.
- Step 1: The Trigger. The bank's real-time fraud detection engine, powered by its own AI, flags a transaction as high-risk. For example, a £1,200 purchase from an online retailer in a different country for a customer who typically only makes small, local purchases.
- Step 2: Instantaneous Voicebot Activation. Within milliseconds of the flag, the system triggers an API call to the voicebot platform (like intervo.ai). The call is initiated to the customer's registered phone number.
- Step 3: The Personalised, Interactive Call. The voicebot doesn't deliver a generic message. It uses text-to-speech (TTS) technology to create a dynamic, data-driven script.
Voicebot: "Hello Alex Smith, this is a critical security alert from Unity Bank. We have just detected a transaction of one thousand two hundred pounds at 'Global Gadgets'. To confirm you authorised this payment, please press 1. If you do not recognise this transaction, press 2 immediately to block your card and speak to our fraud department."
- Step 4: The Logic Tree in Action.
- If Customer Presses 1: The voicebot confirms the action. "Thank you for confirming. The transaction has been approved. You may now hang up." The bot sends a confirmation back to the bank's system, and the transaction is cleared.
- If Customer Presses 2: The voicebot provides immediate reassurance. "Thank you. We have placed an immediate temporary block on your card to prevent further unauthorised use. Please stay on the line, we are connecting you directly to a fraud specialist now." The call is then seamlessly transferred to the highest-priority queue in the human-manned call centre.
- Step 5: Closing the Loop. Regardless of the outcome, the event is logged. The human agent who takes the call already has the full context on their screen: customer name, the fraudulent transaction details, and the fact that the customer has already denied it. No time is wasted asking repetitive questions.
3.1.2 Handling Complex Fraud Scenarios
The logic can be extended to more complex fraud types like Account Takeover (ATO). If the system detects a password reset followed by a login from an unrecognised device and a large fund transfer initiation, the voicebot can be deployed to the original, trusted phone number. The script would be different, focusing on overall account security: "We have detected suspicious activity on your online banking profile... If this was not you, press 2 to immediately freeze all transfers and lock your digital account."
3.2 Use Case: Proactive Management of Service Outages and Downtime
When a core banking system or a digital channel fails, the primary damage is not the technical issue itself, but the chaos and reputational harm caused by a communication vacuum.
3.2.1 Tiered Communication Strategies
A voicebot allows for a sophisticated, tiered communication strategy.
- Tier 1 (Internal): The moment an outage is confirmed, an automated call can be sent to all key internal stakeholders—IT staff, branch managers, and the executive team—ensuring everyone has a consistent and accurate understanding of the situation.
- Tier 2 (High-Value Clients): For wealth management or corporate clients, a personalised call can be made. "Hello, this is an advisory from your relationship management team. We are currently experiencing a technical issue with our wire transfer portal. Our team is working on a resolution with the highest priority and we expect service to be restored within 90 minutes. We apologise for the inconvenience." This level of proactive service is a massive differentiator.
- Tier 3 (General Public): For a widespread outage (e.g., the mobile app is down), a voicebot can be used to update the pre-recorded message on the main customer service line, preventing customers from waiting on hold. "Thank you for calling Unity Bank. We are currently experiencing an issue with our mobile banking app. Our engineers are working to resolve it urgently. There is no need to hold..." This frees up human agents to handle truly unique and complex problems.
3.2.2 The Post-Resolution Follow-up
Equally important is the follow-up. Once service is restored, another mass voice call campaign can be initiated. "This is a follow-up message from Unity Bank. The issue affecting our mobile app has now been resolved. You may log in as usual. We sincerely apologise for the disruption." This closes the communication loop and demonstrates accountability.
3.3 Use Case: Navigating the Complexities of Data Breach Notifications

A data breach is perhaps the most sensitive and damaging crisis a bank can face. Communication must be handled with surgical precision, empathy, and absolute compliance with a complex web of international regulations.
3.3.1 Meeting Global Regulatory Demands with AI
AI voicebots provide a legally defensible and auditable method of fulfilling breach notification requirements swiftly across jurisdictions.
- In Europe (GDPR): Authorities must be notified within 72 hours, and individuals must be notified "without undue delay."
- In the UK (UK-GDPR): Similar stringent 72-hour notification rules apply.
- In the USA: A patchwork of state laws, like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), sets notification timelines.
- In Australia: The Notifiable Data Breaches (NDB) scheme requires prompt notification to affected individuals.
- In India: The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act mandates reporting breaches to the authorities and affected users.
Manually calling thousands or millions of customers to meet these deadlines is impossible. A voicebot system can execute these calls at scale and log every attempt, its duration, and the customer's response, providing a concrete audit trail of the bank's compliance efforts.
3.3.2 Delivering Empathetic and Actionable Guidance
The tone of a data breach notification is critical. Modern TTS engines can be configured with specific tones of voice—calm, serious, and reassuring.
"Hello, this is a very important message from [Bank Name]'s Chief Security Officer. We are calling to inform you about a recent cybersecurity incident... We want to assure you that your account funds are secure... We recommend you take the precautionary step of changing your online banking password. You can do this by visiting our official website at [Bank Website dot com]. Again, that is [spell out the URL]. We have also sent you an email with these instructions. We deeply regret this incident and are here to support you."
This direct, transparent, and guided approach is far more effective than a jargon-filled email that may cause more confusion than clarity.
3.4 Use Case: Business Continuity During Natural Disasters

In an interconnected world, localised disasters can have widespread impact. Whether it's wildfires in California or Australia, hurricanes in the US Gulf Coast, or severe flooding in parts of the UK and Europe, communication is a lifeline. When local infrastructure fails, the basic cellular voice network is often the most resilient channel.
Banks can use geo-fencing data to target customers in affected postcodes, delivering critical information: "This is an emergency alert from [Bank Name] for customers in the [Affected Region]. Due to the ongoing [Disaster Type], our local branches are temporarily closed. Mobile banking services remain fully operational. For emergency assistance, please visit our website. Please stay safe."
3.5 Use Case: Urgent Compliance and Account Security Mandates

Sometimes the emergency is a regulatory deadline. For instance, a central bank mandate might require all customers to update their Know Your Customer (KYC) details by a certain date. As the deadline approaches, voicebots can target the remaining non-compliant customers with an urgent and actionable reminder, far more effective than a final SMS that gets ignored.
Chapter 3: The Architecture of Trust in AI-Driven Communication
Deploying technology is easy. Earning customer trust with it is hard. The success of an AI voicebot system hinges on its ability to build, not erode, trust during a stressful event. This is achieved through careful design principles.
4.1 The Pillars of Digital Trust: Personalisation, Proactivity, and Transparency
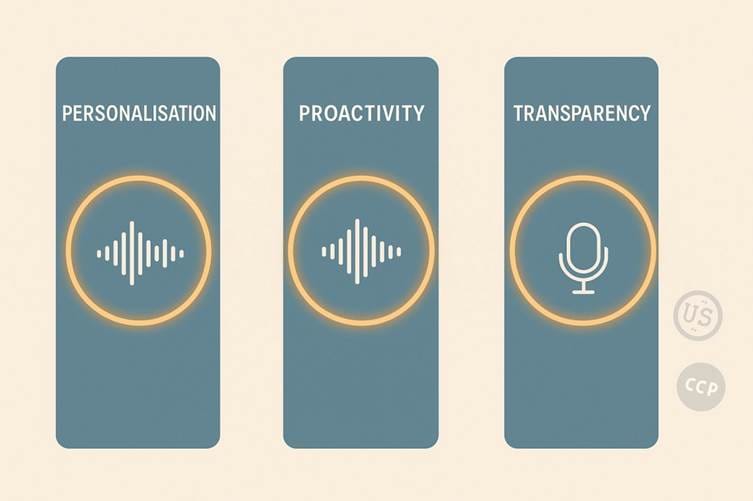
- Personalisation: This goes beyond just using the customer's name. It means referencing the specific event relevant to them. "A transaction of €850," not "a suspicious transaction." This specificity proves the call is legitimate and from a source that has the correct data.
- Proactivity: Trust is built when the bank demonstrates it is watching over the customer's interests. A proactive call about a potential issue before the customer even notices it transforms the bank from a passive service provider into an active guardian.
- Transparency: The voicebot should immediately identify itself and its purpose. "This is an automated security alert from..." There should be no attempt to trick the user into thinking they are talking to a human. Being upfront about the nature of the call builds credibility and manages expectations.
4.2 Engineering Empathy: The Nuances of Conversational Design

While a bot cannot feel empathy, it can be designed to project it. This is a function of high-quality conversational design (CxD).
- Voice and Pacing: Modern Neural TTS engines can produce voices that are warm, calm, and clear, with culturally appropriate accents (e.g., standard American, British RP, Australian English). The pacing of the speech can be controlled—slowing down when reading out important numbers or URLs, and adding slight pauses to mimic natural human speech.
- Language: The language should be simple, direct, and free of technical jargon. In a stressful situation, clarity trumps verbosity. The script should be written from a place of "how can we help and reassure you?"
- Acknowledging the Situation: Simple phrases like, "We understand this may be concerning," or "We apologise for this disruption," can have a significant impact on the customer's perception of the call.
4.3 The Human-in-the-Loop Model: The Perfect Symbiosis

The most successful AI strategies are not about replacing humans, but augmenting them. The AI voicebot is the perfect "Tier 1" agent. It handles the massive scale of initial contact and filters the issue. The human agent is the "Tier 2" specialist, reserved for situations that require creativity, complex problem-solving, and genuine human connection.
A platform like intervo.ai is designed around this seamless handover. The AI gathers the initial data, authenticates the user, and provides the context, so when the call is transferred, the human agent is empowered to solve the problem immediately. This hybrid model offers the best of both worlds: the scale and speed of a machine, with the wisdom and empathy of a human expert.
Chapter 4: A Strategic Roadmap for Implementing an AI Voicebot Alert System
Adopting this technology requires more than just buying software; it demands a strategic, phased approach to ensure successful integration and adoption.
5.1 Phase 1: Defining Objectives and Measurable KPIs
Before a single line of code is written, the bank must define what success looks like.
- Objectives: What is the primary goal? To reduce fraud losses? To improve customer satisfaction during outages? To meet a regulatory deadline?
- KPIs (Key Performance Indicators): These must be specific and measurable. Examples include:
- Reduction in average fraud detection-to-resolution time (from hours to minutes).
- Decrease in call volume to human agents during a service outage by X%.
- Increase in Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) scores related to problem resolution.
- Compliance adherence rate for breach notifications.
5.2 Phase 2: Selecting the Right Technology Partner
Not all voice AI platforms are created equal. Key criteria for selection should include:
- Security and Compliance: Does the vendor have certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and are they compliant with data protection laws across all your operating regions (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)?
- Scalability and Reliability: Can the platform handle hundreds of thousands of concurrent calls with guaranteed uptime and global points of presence?
- Voice Quality and Language Support: Does it offer high-quality, natural-sounding TTS voices in all the languages and major accents your customers speak?
- Integration Capabilities: Does it have robust APIs that can easily integrate with the bank's existing Core Banking System (CBS), CRM, and fraud detection engines?
- Analytics and Reporting: Does it provide a detailed dashboard to track the KPIs defined in Phase 1?
5.3 Phase 3: Secure Data Integration and Infrastructure
This is the most critical technical phase. The voicebot platform needs secure, real-time access to specific data points (like customer name, transaction details) to personalise the calls. This is typically done via secure APIs. The bank's IT and security teams must work closely with the vendor to ensure the data pipelines are encrypted, authenticated, and resilient.
5.4 Phase 4: Crafting Intelligent and Dynamic Conversation Flows
This is where the user experience is designed. For each use case, a conversation "flow" or "script" must be developed. This involves:
- Writing the base script.
- Defining the interactive options ("Press 1, Press 2...").
- Mapping out the logic for each customer response.
- Designing the seamless handover process to human agents.
5.5 Phase 5: Pilot Testing, Learning, and Iteration
Never launch a system like this to all customers at once. Start with a small, controlled pilot programme.
- Select a limited use case (e.g., alerts for a specific type of transaction).
- Target a small segment of customers.
- Run the pilot and meticulously analyse the results against the KPIs.
- Gather feedback. Did customers understand the call? Was the voice clear? Did they take the correct action?
- Use A/B testing to try different scripts or voice tones to see which performs better.
- Iterate on the design based on this real-world feedback.
5.6 Phase 6: Scaling for a Resilient Future
Once the pilot has proven successful and the model has been refined, the system can be scaled. This involves rolling it out to more customers, applying it to other use cases, and deeply embedding it as a core component of the bank's operational and crisis management framework.
Chapter 5: The Tangible ROI: Building the Business Case for Voice AI
An investment in an advanced voice AI platform is not an expense; it is a strategic investment with a clear and compelling Return on Investment (ROI).

6.1 Quantifying Cost Reductions
- Fraud Loss Prevention: This is the most direct ROI. Preventing a single large fraudulent transaction can often pay for the system for a year. By reducing the time-to-resolution, the overall financial losses from fraud are drastically cut.
- Reduced Call Centre Load: By automating Tier 1 alert calls, the volume of inbound calls to expensive human agents is significantly reduced, both during crises and for routine follow-ups. This allows the bank to do more with its existing staff.
- Lower Compliance Fines: By ensuring timely, auditable, and compliant notifications during data breaches, the bank mitigates the risk of massive regulatory fines across multiple jurisdictions.
6.2 Measuring Gains in Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
- Improved Customer Retention: A customer whose fraud is stopped instantly feels protected and valued. This single positive experience can secure their loyalty for years. Conversely, a poor experience during a crisis is one of the leading causes of customer churn.
- Enhanced Brand Reputation: A bank that communicates proactively and effectively during a crisis is seen as competent, modern, and trustworthy. This strong reputation attracts new, high-value customers.
- Increased Share of Wallet: Trust is the currency of banking. When customers trust their bank's security, they are more likely to consolidate more of their financial life with that institution (e.g., loans, investments, insurance).
6.3 De-risking the Enterprise
Beyond direct costs and revenues, voice AI significantly reduces two major forms of risk:
- Operational Risk: It automates a critical process, reducing the chance of human error and removing the bottleneck of manual call centres.
- Reputational Risk: In the age of social media, news of a poorly handled crisis can spread globally in minutes. A swift, professional, and effective communication strategy is the best defence against reputational damage.
7. Conclusion: The Future of Secure Banking is Not Just Digital, It's Vocal

The evolution of banking has been a relentless march towards digitization and automation. Yet, in our pursuit of efficiency, we risk losing the human element of communication, especially when it matters most. AI voicebots represent a remarkable synthesis—a way to reclaim the power and immediacy of the human voice and deploy it with the speed and scale of a machine.
For banks today, adopting a sophisticated voice AI strategy for emergency alerts is no longer a matter of 'if' but 'when'. It is the most effective technology available to combat machine-speed threats, manage operational crises with grace, and, most importantly, build a foundation of unwavering trust with the customer. The tools of yesterday—SMS and email—are now the liabilities of today. The future of secure, resilient, and customer-centric banking will not be silent; it will be vocal.
Is your bank's communication strategy prepared for the next critical alert? Explore how intervo.ai can equip you with the intelligent voice solutions needed to protect your customers and your reputation in the moments that matter.
Visit intervo.ai to learn more or test it yourself.
References
- Deloitte Center for Financial Services. (2024). Trust and Transformation in the Global Banking Industry.
- IBM Security. (2025). Annual Cost of a Data Breach Report: A Financial Sector Analysis.
- McKinsey & Company. (2024). Conversational AI: The New Face of Customer Engagement in Banking.
- Gartner Research. (2025). Market Guide for Conversational AI Platforms.
- Official Journals and Gazettes for: GDPR (EU), UK-GDPR (UK), CCPA (California, USA), Privacy Act 1988 (Australia), DPDP Act (India).
- Financial Brand Forum. (2025). Global Trends in Digital Banking Customer Experience and Crisis Communication.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Are AI voicebots secure and compliant across different regions like the US, Europe, and Australia?
A: Yes, provided you choose a reputable partner. Leading platforms like intervo.ai are built on a "security-first" architecture designed for global compliance. This includes end-to-end encryption, certifications like ISO 27001 and SOC 2, and features that help banks adhere to regional data protection laws like GDPR, CCPA, and others. The platform should also support data residency requirements, allowing data to be processed and stored within a specific region if required.
Q2: Won't customers in different cultures react differently to a "robot" call?
A: This is a crucial consideration. The key is relevance, quality, and cultural nuance. The system's value is universal: an alert about potential fraud is welcomed in London just as it is in New York or Mumbai. The difference is in the delivery. Advanced platforms allow for customisation of voice type, accent (e.g., a British, American, or Australian accent), and pacing to feel more natural and appropriate for the target audience, ensuring the call is perceived as a valuable service, not a generic, impersonal intrusion.
Q3: How is an AI voicebot different from the standard IVR our bank already has?
A: The difference is profound. A traditional IVR (Interactive Voice Response) is a passive, inbound system with a rigid menu tree ("Press 1 for balances, Press 2 for..."). An AI voicebot is an outbound, proactive, and intelligent conversational agent. It can initiate thousands of calls simultaneously, personalise each call with real-time data, understand customer responses (via keypad or natural language), and make intelligent decisions based on that input, such as transferring to a specific human agent. It's the difference between a static phone directory and an intelligent personal assistant.
Q4: Can the system handle the diverse languages and accents needed for a global operation?
A: Yes. This is a core requirement for any global enterprise. Top-tier voice AI platforms use state-of-the-art Neural Text-to-Speech (TTS) engines that can generate crystal-clear, natural-sounding speech in dozens of languages and a wide variety of accents. This ensures that the critical message is understood clearly by customers whether they are in Sydney, Singapore, Dublin, or Delhi.
Q5: What is the typical implementation timeline for a system like this for a multinational bank?
A: The timeline can vary based on the complexity of the bank's internal systems, but it's faster than most people think. With a modern, API-first platform, a pilot programme for a single use case (like fraud alerts in one country) can often be designed, integrated, and launched in as little as 6-8 weeks. The phased approach outlined in this guide allows for rapid initial deployment and value realisation in one market, followed by a more measured, strategic rollout to other regions and use cases.